Platform Walkthrough
The sidebar panel on the left lets you navigate to different sections of the BaseRock portal and access all functionalities.
Business Flows:
This section allows users to generate use cases from a given PRD document and map the corresponding AI-generated test scripts to create a Requirement Traceability Matrix.
Services:
The Services section lists all services that BaseRock has learned from the source code.
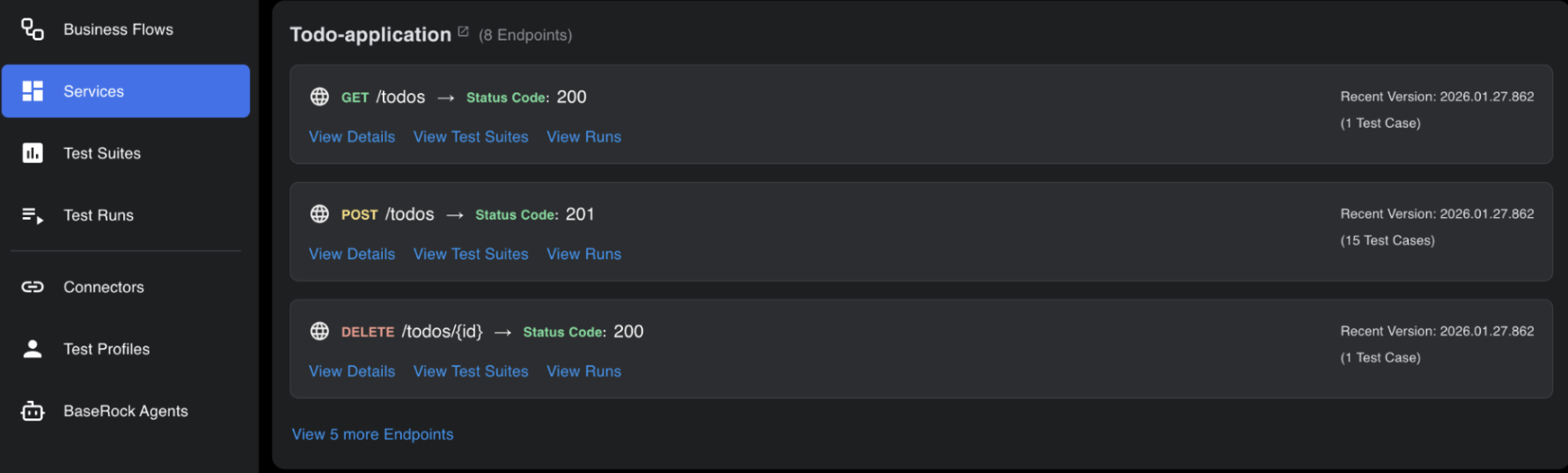
This page shows all services under test for your applications, with infinite scroll and corresponding versions displayed alongside.
To see more information about a service, click its name or “View x more endpoints”. Clicking the service name opens the page shown below.
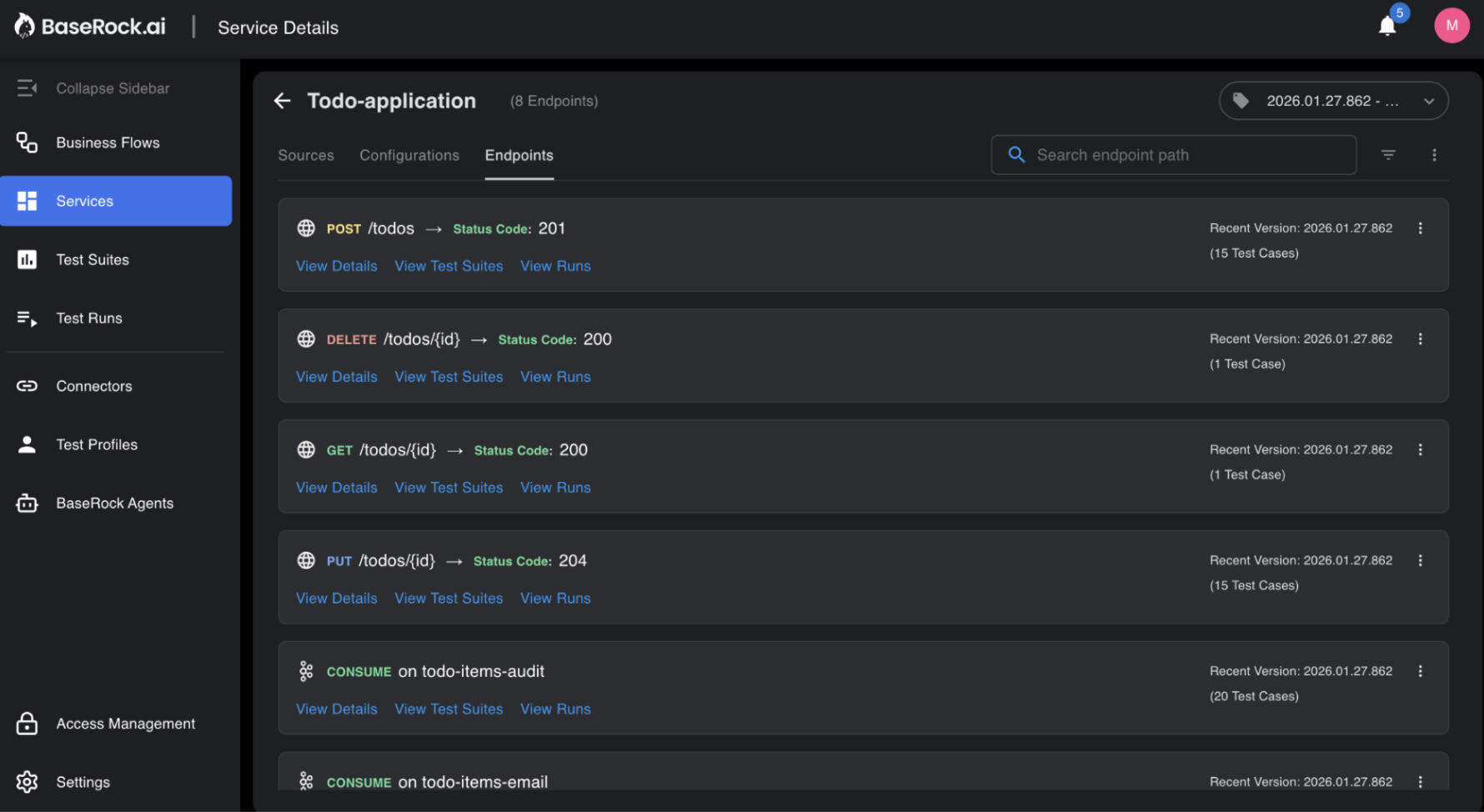
There are three tabs within a service - Sources, Configurations and Endpoints.
Sources :
It shows how BaseRock has learned about the service and how you can provide more context via a requirement document.
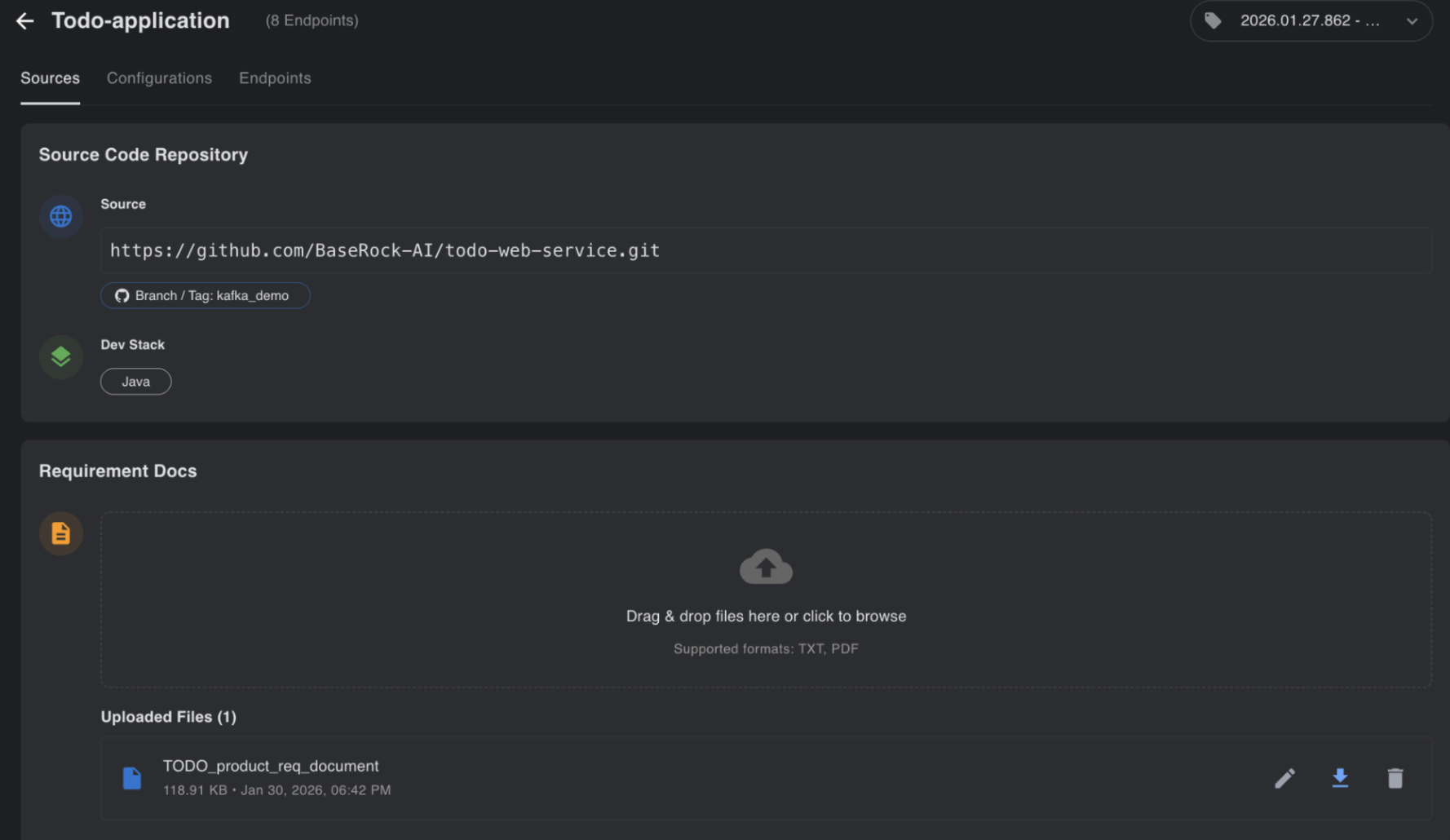
Another example of BaseRock’s learning via Github repository is shown above under the sources tab of the service.
Versioning: Users can maintain different versions of branches of the service to make sure the test cases generated for previous versions stay intact and do not get updated without approval.
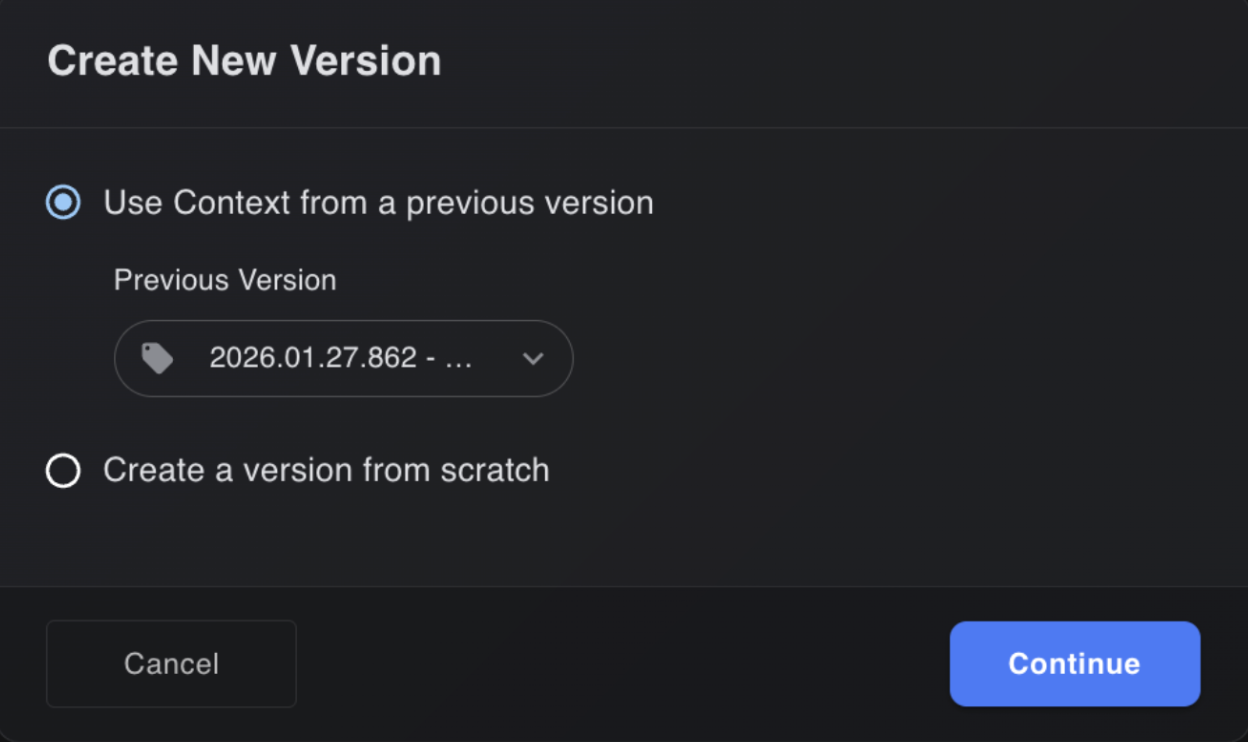
A versioning use case: the first time a service is set up with a main branch, and later a feature branch with significant changes needs to be tested without changing the previous test cases generated for the main branch.
This highlights the need for version-aware testing to support parallel validation across code branches.
Configurations:
The next tab is Configurations, where you can define additional context variables and their values (static or dynamic via instructions) for performing computations or providing actions via playbook. Check section: Best practices for using variables in BaseRock.
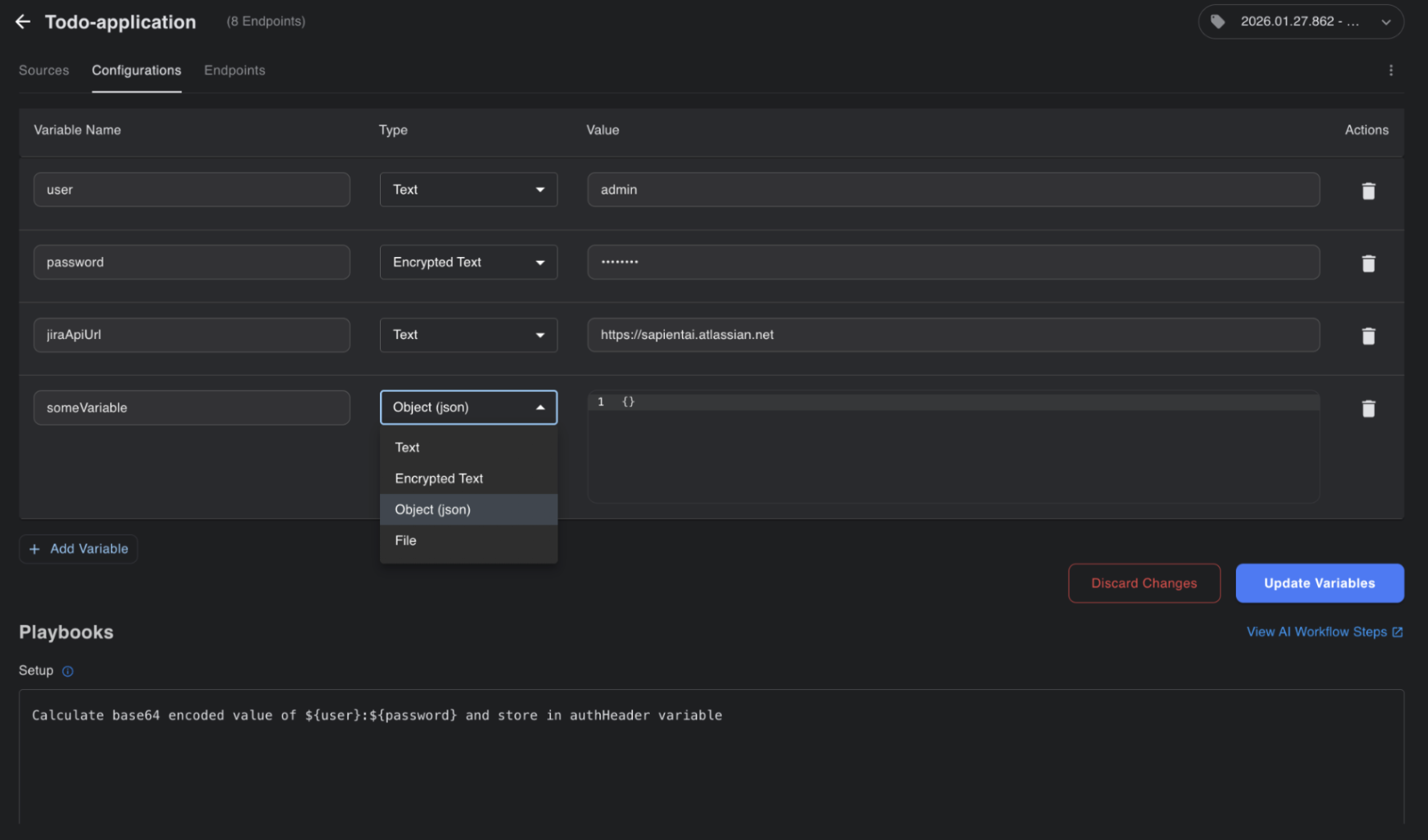
For example, you can create variables for credentials, such as an authentication token that must be passed in the API request payload before sending it.
Open-Questions:
Open questions help BaseRock bridge the context gap between what it has learned from the source code and the information needed to run end-to-end flows.
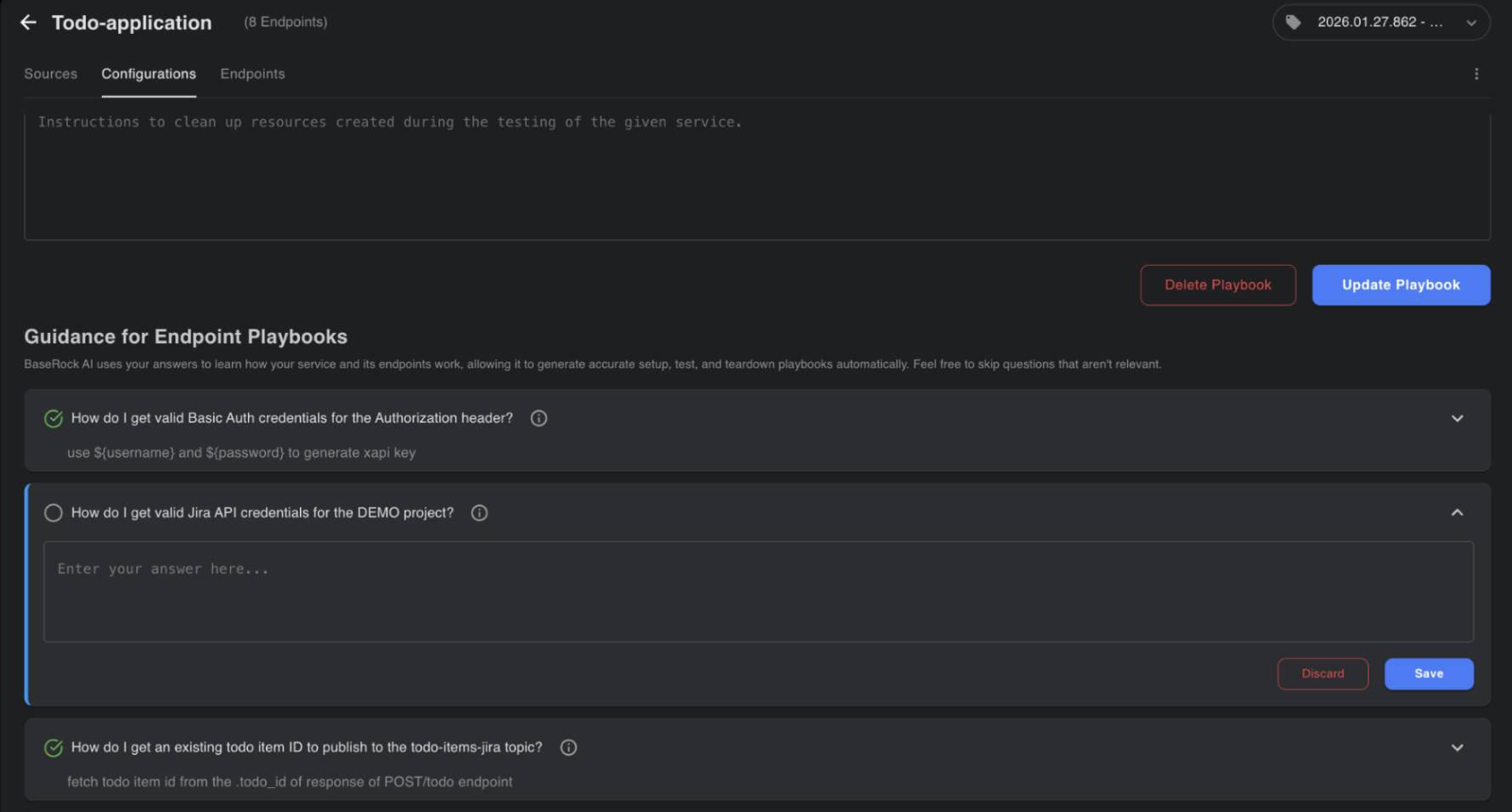
Open questions can be answered in simple, plain English—either by providing answers directly or by performing actions to fetch answers at runtime.
Endpoints:
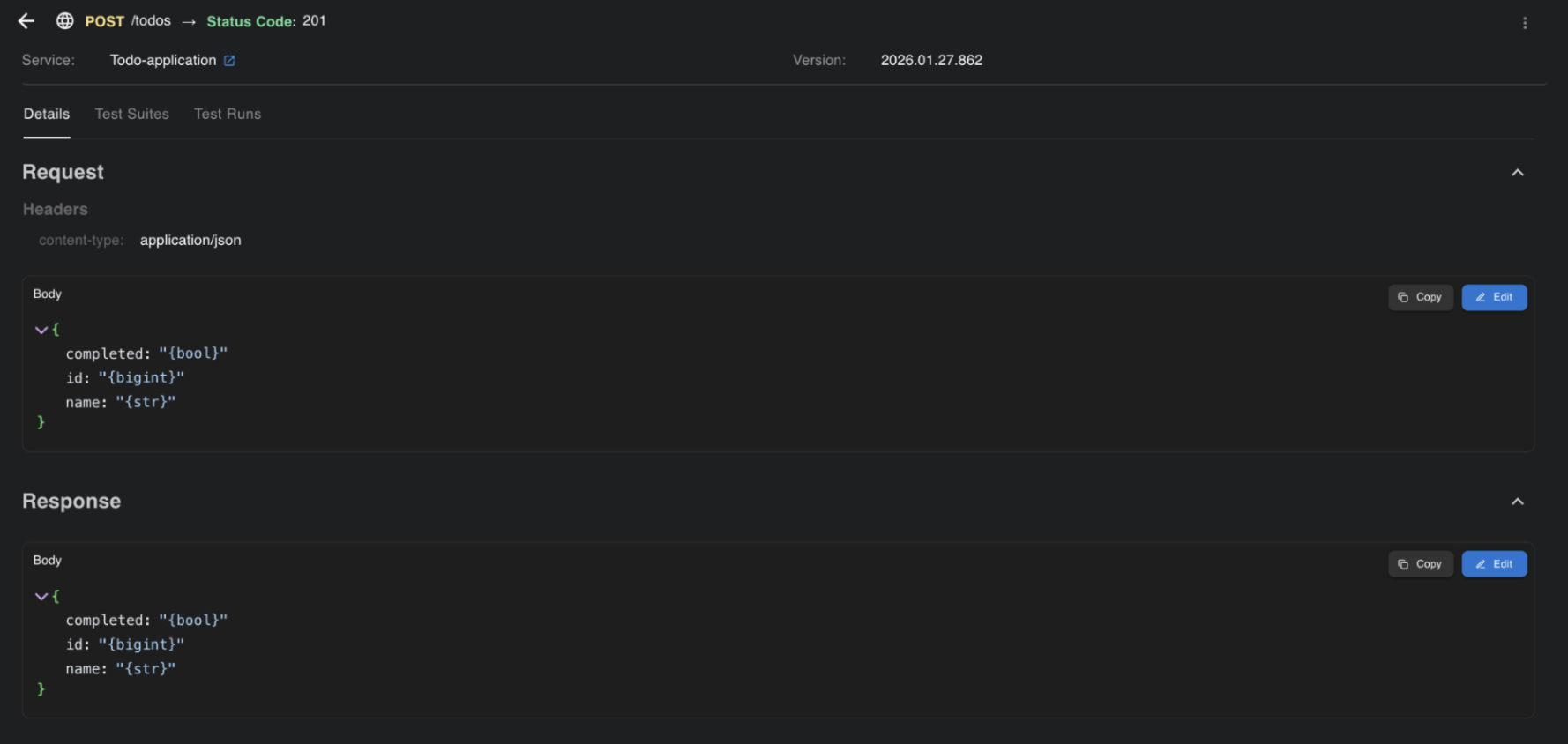
The third tab within a service is Endpoints, where all APIs, Kafka topics, etc. are shown based on what BaseRock has learned (see the images).
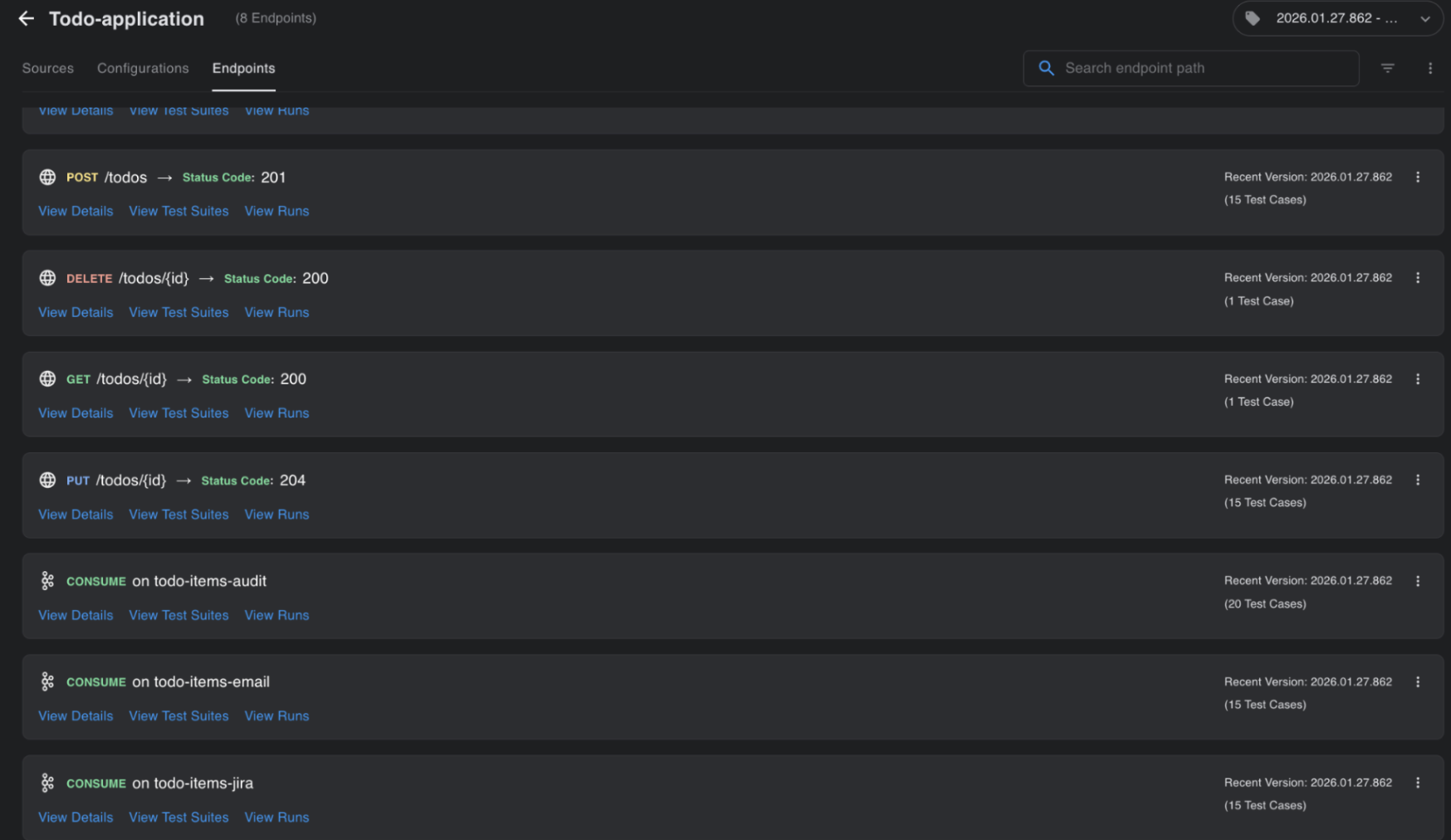
Each endpoint shows its details, test scripts covering positive, negative, and edge cases, and execution results of test runs.
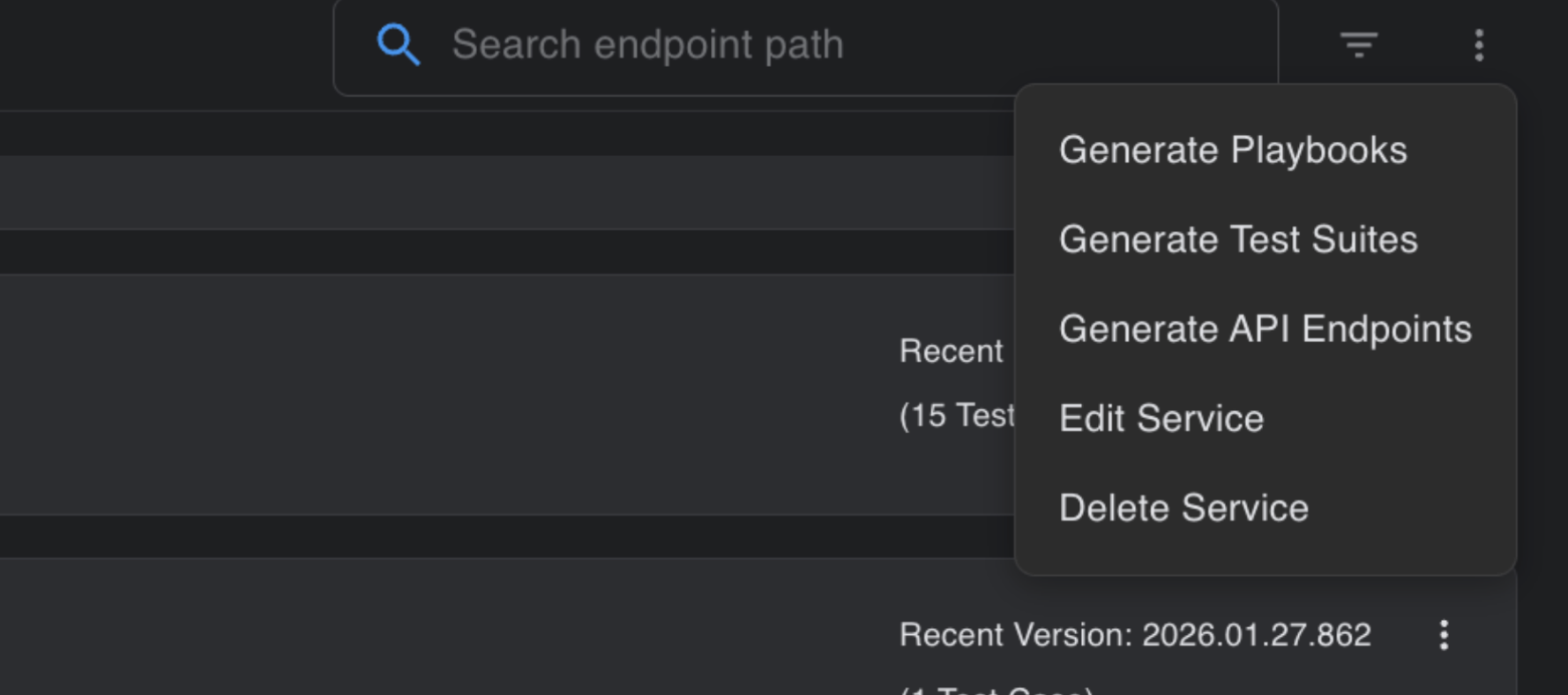
The three dots in the top-right corner of the Endpoints tab give users options to Generate Playbook, Generate test suite, rediscover API endpoints, download test cases, and modify the service.
The prompt area when generating test cases lets users add their domain expertise and business-specific validations to the test cases.
Check section: Test Case Generate to learn how to leverage prompts to generate quality and desirable test cases.
Within an endpoint, you can verify the schema, which is used to generate different types of payloads and test cases.
Test Cases:
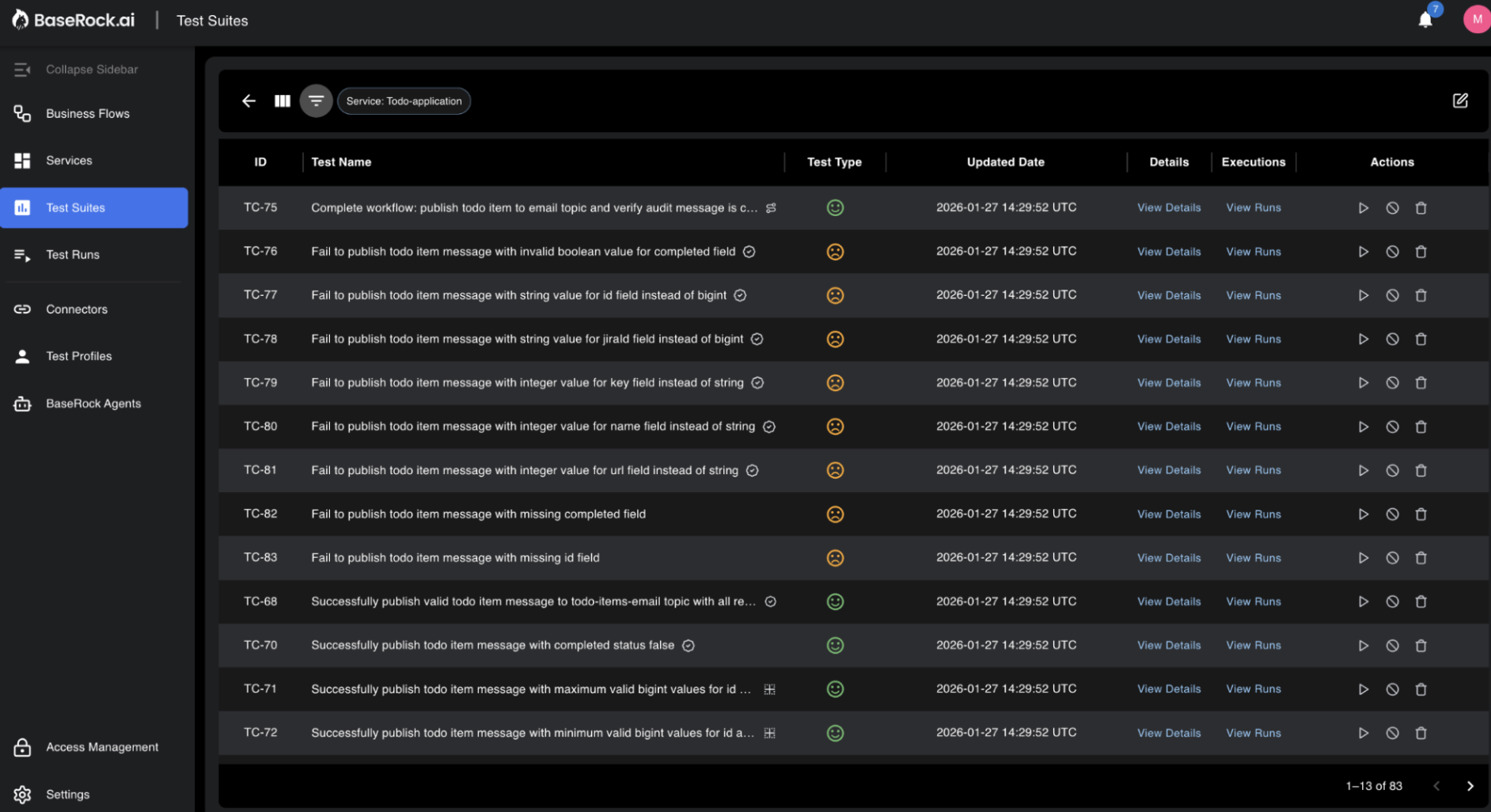
This section consolidates all test cases from all services in BaseRock. You can use filters to find the desired tests and customize how the table is displayed.
Test Runs:
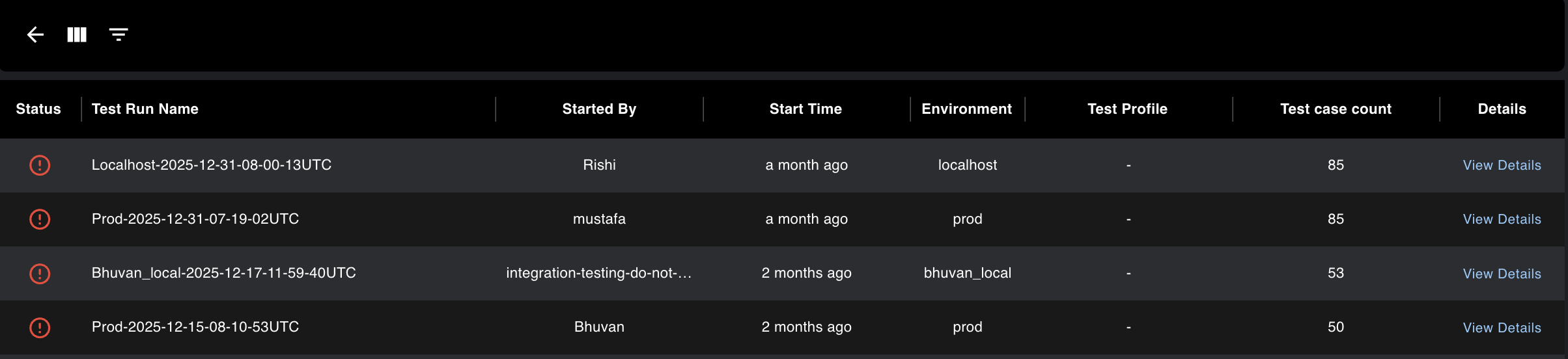
This section stores all the test results belonging to any service or suite. The table contains all test runs. When you open a test run, you will see all the test cases that were executed in it. The status of a test run will be failed even if a single test case fails inside it. You can filter and view results by test type, service, and other criteria.
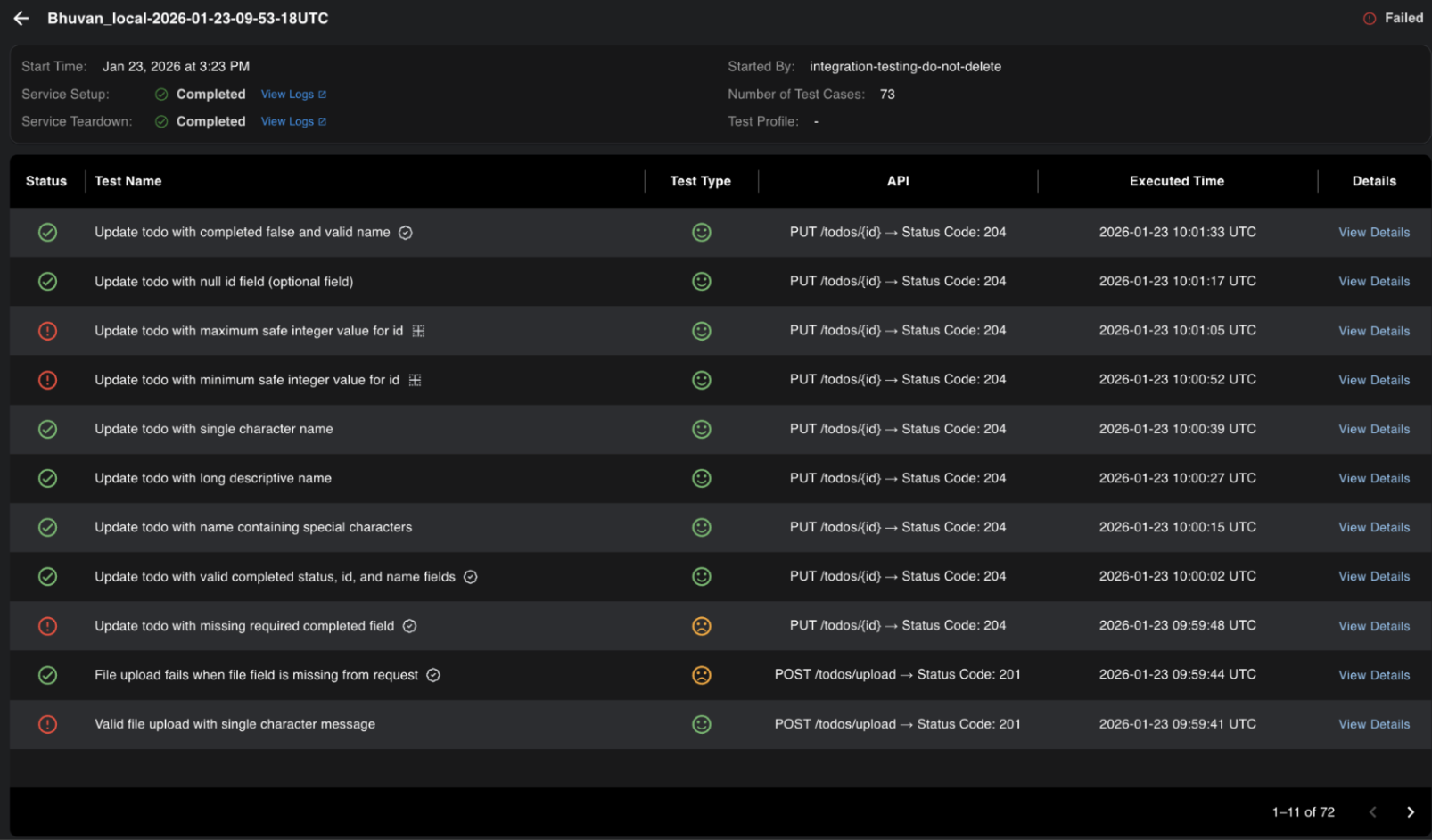
Below are the test case runs inside a particular test run.
Connectors:
Connectors allow BaseRock to connect with git and learn from the source code (read-only).
Check the section for more details on how to use connectors: Add Connector
Test profiles:
Test profiles let you store environment settings that can be changed when running test cases. For example, a UAT environment may have different configurations than pre-production.
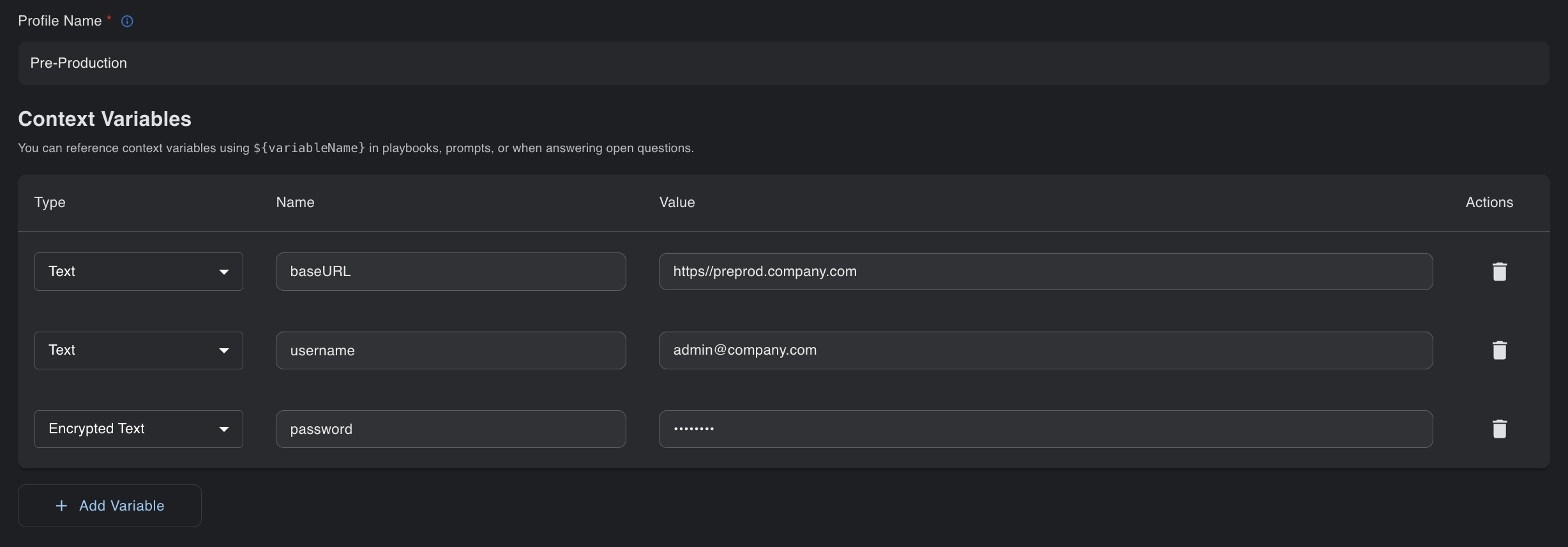
Access management:
There are two types of users in BaseRock: - Administrators—Can add service accounts and modify LLM keys in use - Users—Regular users of BaseRock with full access except for the above
Check the section to know how to add a team member to BaseRock: Invite Team members
Settings:
Settings allow administrators to add the LLM provider to BaseRock and get started without external assistance.
Check the section to know how to Setup LLM Provider